
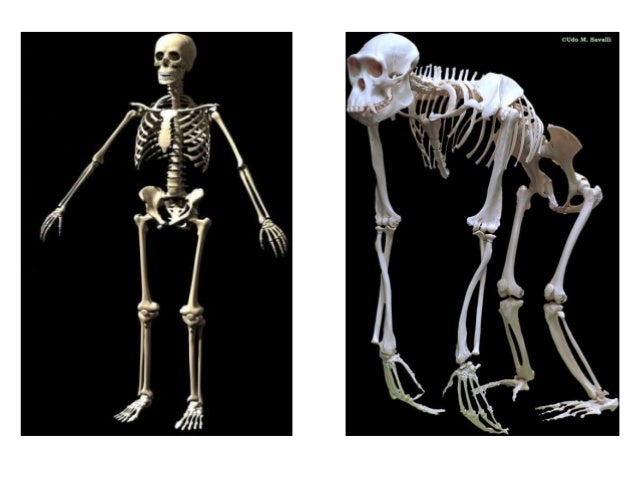
However, terrestrial quadrupedialism is used to travel between resource rich localities. Like the other apes, chimpanzees engage in suspensory behavior frequently. Sticks are used to fish out termites from logs or ants from anthills and rocks are used to crush nuts with a hard shell. Tool use is well documented among chimps, typically in food acquisition. Males are slightly larger than females with males weighing about 43 kg and females about 34 kg (Smith and Jungers, 1997).Ĭhimpanzees eat a wide variety of food including, fruits, nuts, leaves, insects, and smaller bodied mammals (Fleagle, 1999). Chimpanzees exhibit a moderate degree of sexual dimorphism. Social groups are based in male philopatry, meaning that males remain in their natal group, while females migrate to new communities (Fleagle, 1999). In fission-fusion societies, group composition is constantly in flux and is typically dependent upon resource availability. Chimpanzees are most commonly depicted as living in rainforests however, several populations live in woodlands and dry savannahs where tree are sparse (Fleagle, 1999).Ĭhimpanzees live in multi-male multi-female groups that are often defined as fission-fusion. In addition to having a wide distribution across the continent, chimpanzees live in diverse habitats. The geographical distribution of chimpanzees ranges across Sub-Saharan Africa from Senegal in the west to Tanzania in the east. Therefore, although the last common ancestor between humans and African apes is believed to exist between five and six million years ago, there is no consensus as to what this common ancestor would have looked like (Fleagle, 1999 Hartwig, 2002). Additionally, no fossil specimens from more recent epochs exhibit derived traits that can be linked to the African apes. The Miocene apes do not have derived morphology that is shared with the African apes and therefore none of the Miocene specimens can be categorized as ancestral to the African ape lineage. The fossil record indicates that African homonoids arrived in Europe during the Miocene between 16 and 17 million years ago, followed by a diversification of apes across Europe and Western Asia (Hartwig, 2002). Additionally, fossil apes have been discovered throughout Europe, distributed between the French and Spanish Pyrenees to the Republic of Georgia. Although the best record of proconsulids is found in Africa, specimens have also been found in Asia, suggesting that proconsulids migrated to Asia in the early Miocene (Fleagle 1999). The first radiation of fossil apes, the proconsulids, occurred in Africa from the late Oligocene to the middle Miocene. Finally, unlike all other primates, apes lack a tail (Fleagle, 1999).Īlthough there are only five extant ape genera, several ape genera have been identified in the fossil record. Apes also have a broad, short thorax, as opposed to the long, narrow thorax found in monkeys. These anatomical features enable apes to have a wide range of overhead movement and aid in suspensory locomotion. In addition to having long forelimbs, apes have a dorsally positioned scapula and globular humeral head. Relatively long forelimbs are attributed to the highly suspensory behavior of all non-human apes. First, apes typically have longer forelimbs than hindlimbs, the only exception to this trend being humans. Apes are anatomically distinct from monkeys in several ways. Hominoidea includes gibbons and siamangs (Hylobatidae), commonly referred to as the lesser apes, and orangutans ( Ponginae), gorillas, chimpanzees, bonobos, and humans ( Homininae), often referred to as the great apes (Hartwig, 2002). Right and left skeleton of the leg (to be attached via the joint connections on the body)īase with stand (the scope of delivery includes assembly instructions for the base and stand.Chimpanzees ( Pan troglodytes) are apes and belong to Hominoidea. Right and left skeleton of the arm (to be attached via the joint connections on the body), Skull (to be fitted onto the base via the opening in the calvarium), This SOMSO Artificial Skeleton of a Chimpanzee is delivered mounted, with the following exceptions: The right and left foot can be detached from the leg. Joints mounted and movable, upper and lower extremities removable. Showing life-size all the anatomical details of the bone structure. Pan troglodytes, Natural cast of the bones of an adult male, made in SOMSO-Plast®. SOMSO Artificial Skeleton of a Chimpanzee Adam-Rouilly Clinical Skills Simulators.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
